前端面试中,手撕代码环节除了力扣上的算法题目之外,还有一些针对前端知识点的题目,大致有以下几类:
- 算法类
- 原理类
- 应用类
算法类
1. 手写快排、冒泡、选择排序
/**
* --- 测试用例 ---
*
* 输入:[1, 34, 5, 76, 8, 6, 9, 7, 6, 3]
* 输出:[1, 3, 5, 6, 6, 7, 8, 9, 34, 76]
*
* --- 说明 ---
*
* 思考:快速排序是稳定的吗?
* 解答:base 的每次选择,会导致快排是不稳定排序。
*/
const quickSort = (nums) => {
if (nums.length < 2) {
return nums;
} else {
var left = [];
var right = [];
var pivot = Math.floor(nums.length / 2); // Math.floor 向下取整
var base = nums.splice(pivot, 1)[0];
for (let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] < base) {
left.push(nums[i]);
} else {
right.push(nums[i]);
}
}
}
return quickSort(left).concat([base], quickSort(right));
}2. URL 拆解问题
/**
* --- 题目描述 ---
*
* 实现一个函数,可以对 url 中的 query 部分做拆解,返回一个 key: value 形式的 object
*
* --- 实例 ---
*
* 输入:'http://sample.com/?a=1&e&b=2&c=xx&d#hash'
* 输出:{a: 1, b: 2, c: 'xx', d: ''}
*/
function getQueryObj(url) {
// TODO
let arr = url.split('?')[1].split('#')[0].split('&');
const res = {};
arr.forEach(e => {
const [key, value] = e.split('=');
if (!value) {
res[key] = '';
} else {
res[key] = value;
}
})
return res;
}3. 将 HTTP header 转换成 js 对象
/**
* --- 题目描述 ---
*
* 实现一个方法,把 HTTP 文本形式(字符串)的 header 转换成 JS 对象。
*
* --- 测试用例 ---
*
* 输入:
* `Accept-Ranges: bytes
* Cache-Control: max-age=6000, public
* Connection: keep-alive
* Content-Type: application/javascript`
* 输出:
* {
* "Accept-Ranges": "bytes",
* "Cache-Control": "max-age=6000, public",
* Connection: "keep-alive",
* "Content-Type": "application/javascript"
* }
*
* --- 解题思路 ---
*
* 1. 首先将每行数据作为数组的一个元素
* 2. 将每个元素使用冒号分割,前面为 `key`,后面为 `value`。
*/
const solution = (s) => {
let res = {};
let arr = s.split("\n");
arr.forEach((e) => {
let tmp = e.split(": ");
res[tmp[0]] = tmp[1];
})
return res;
}
注意到
`xxxxxx
xxxxx
xxxx`这样的输入格式叫做 模板字符串。
输出如下:
{
'Accept-Ranges': 'bytes',
'Cache-Control': 'max-age=6000, public',
Connection: 'keep-alive',
'Content-Type': 'application/javascript'
}注意到上面的输出结果中,Connection 没有带引号,这是为什么呢?
4. 将数组转化为树形结构
初始时,数组中的每个元素具有 4 个属性,其中有 id 和 parent_id,现在我们需要根据这两个 id 之间的关系,添加一个 children 属性,使之成为一棵树的结构。
比如有如下数据:
var menu_list = [{
id: '1',
menu_name: '设置',
menu_url: 'setting',
parent_id: 0
}, {
id: '1-1',
menu_name: '权限设置',
menu_url: 'setting.permission',
parent_id: '1'
}, {
id: '1-1-1',
menu_name: '用户管理列表',
menu_url: 'setting.permission.user_list',
parent_id: '1-1'
}, {
id: '1-1-2',
menu_name: '用户管理新增',
menu_url: 'setting.permission.user_add',
parent_id: '1-1'
}, {
id: '1-1-3',
menu_name: '角色管理列表',
menu_url: 'setting.permission.role_list',
parent_id: '1-1'
}, {
id: '1-2',
menu_name: '菜单设置',
menu_url: 'setting.menu',
parent_id: '1'
}, {
id: '1-2-1',
menu_name: '菜单列表',
menu_url: 'setting.menu.menu_list',
parent_id: '1-2'
}, {
id: '1-2-2',
menu_name: '菜单添加',
menu_url: 'setting.menu.menu_add',
parent_id: '1-2'
}, {
id: '2',
menu_name: '订单',
menu_url: 'order',
parent_id: 0
}, {
id: '2-1',
menu_name: '报单审核',
menu_url: 'order.orderreview',
parent_id: '2'
}, {
id: '2-2',
menu_name: '退款管理',
menu_url: 'order.refundmanagement',
parent_id: '2'
}
]思路是先使用 tmp 将数组中的元素处理成 id: {id...menu_name...menu_url...parent_id} 类的格式,然后针对该数据处理成树状结构。
实现代码如下:
const buildTree = (arr) => {
tmp = {};
res = {};
for (let i in arr) {
tmp[arr[i].id] = arr[i];
}
for (let i in tmp) {
if (tmp[i].parent_id) { // 如果节点没有父节点,即该节点为根节点
if (!tmp[tmp[i].parent_id].children) { // 该节点的父节点和该节点没有形成关系
tmp[tmp[i].parent_id].children = new Object();
}
tmp[tmp[i].parent_id].children[tmp[i].id] = tmp[i];
} else {
res[tmp[i].id] = tmp[i];
}
}
return res;
}
console.log(buildTree(menu_list)); //测试代码,menu_list 为前面的数据。据说这个代码可以使用数组的方法 Array.prototype.find() 来美化代码。如何实现呢?其实我也没太想好😂欢迎讨论。
5. 数组扁平化
解法一:递归
var arr = [1, [2, [3, 4]]];
function flatten(arr) {
var result = [];
for (var i = 0, len = arr.length; i < len; i++) {
if (Array.isArray(arr[i])) {
result = result.concat(flatten(arr[i]))
}
else {
result.push(arr[i])
}
}
return result;
}
console.log(flatten(arr))解法二:es6 拓展运算符
var arr = [1, [2, [3, 4]]];
function flatten(arr) {
while (arr.some(item => Array.isArray(item))) {
arr = [].concat(...arr);
}
return arr;
}
console.log(flatten(arr))原地解法:这是一次面试中,面试官看完递归解法之后,问我有没有原地解法。这也是感到迷惑的地方,目前猜测可能是想考察 flat 的用法。欢迎讨论。
const arr1 = [0, 1, 2, [[[3, 4]]]];
console.log(arr1.flat(3)); // 3 代表数组内最多嵌套层数
// expected output: [0, 1, 2, 3, 4]6. 模拟 lodash 中的 _.get() 函数
/**
* --- 题目描述 ---
*
* 补充函数的 TODO 部分,模拟 lodash 中的 _.get() 函数。
*
* --- 测试用例 ---
*
* 输入:
* const obj = { selector: { to: { toutiao: "FE Coder"} }, target: [1, 2, { name: 'byted'}]};
* get(obj, 'selector.to.toutiao', 'target[0]', 'target[2].name')
* 输出:
* ['FE coder', 1, 'byted']
*/
function get(object, ...path) {
return path.map((item) => {
item.replace(/\[/g, ".")
.replace(/\]/g, "")
.split('.')
.map(path => object = object && object[path]);
return object;
})
}原理类
1. 深拷贝
// deepClone
function deepClone(obj = {}) {
if (typeof obj !== 'object' || obj == null) {
// obj 是 null 或者不是对象和数组,直接返回
return obj;
}
let res;
if (obj instanceof Array) {
res = [];
} else {
res = {};
}
for (let key in obj) {
// 判断自身中是否包含自身属性
if (obj.hasOwnProperty(key)) {
res[key] = deepClone(obj[key])
}
}
return res;
}
// 验证
o = {a: 1, d: {c: '4'}};
res = deepClone(o);
console.log(res);
console.log(res == o);2. 浅拷贝
代码出处:https://dmitripavlutin.com/javascript-shallow-clone-objects/
// 首先定义一个对象
const hero = {
name: 'Batman',
city: 'Gotham'
};
// **********************方法一**********************
const heroEnhancedClone = {
...hero,
name: 'Batman Clone',
realName: 'Bruce Wayne'
};
// 验证
heroEnhancedClone; // { name: 'Batman Clone', city: 'Gotham', realName: 'Bruce Wayne' }
// **********************方法二**********************
const { ...heroClone } = hero;
// 验证
heroClone; // { name: 'Batman', city: 'Gotham' }
hero === heroClone; // => false
// **********************方法三**********************
const hero = {
name: 'Batman',
city: 'Gotham'
};
// 验证
const heroClone = Object.assign({}, hero);
heroClone; // { name: 'Batman', city: 'Gotham' }
hero === heroClone; // => false3. 手写 bind 函数
// 模拟 bind
Function.prototype.bind1 = function() {
// 将参数拆解为数组
const args = Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments) // 变成数组
// 获取 this(数组第一项)
const t = args.shift()
// fn1.bind(...) 中的 fn1
const self = this
// 返回一个函数
return function() {
return self.apply(t, args)
}
}
function fn1(a, b, c){
console.log('this', this)
console.log(a, b, c)
return 'this is fn1'
}
const fn2 = fn1.bind1({x: 100}, 10, 20, 30)
const res = fn2()
console.log(res) 4. 手写 new
答案
function funcNew(obj, ...args) {
const newObj = Object.create(obj.prototype);
const result = obj.apply(newObj, args);
return (typeof result === 'object' && result !== null) ? result : newObj;
}解读
先通过一个例子来理解 new 的作用吧:
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}
Person.prototype.sayName = function() {
console.log(this.name);
}
const p = new Person('orange')
console.log(p.name) // 'orange'
p.sayName(); // 'orange'代码中我们新建了一个对象 Person,它具有属性 name,且在 Person.prototype 上定义了函数 sayName。
当我们通过 new 创建一个新的实例 p 时,便同时具有了属性 p.name 和 p.sayName(),关系如下图:

知道了原理,就可以自己实现了。也就是说,自己写一个函数 funcNew(),使得 const p = new Person('orange') 和 const p = funcNew('orange') 得到的 p 完全相同,于是得到了答案中的代码。
答案中最后一行代码如何理解?
前面的例子我们只考虑了 Person 中没有返回值的情况,如有有返回值,new 一个实例将会受到 Person 中返回值的影响。比如说:
/**
* --- Person 中 return 一个对象,p 为该对象 ---
*/
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
return {age: 35}
}
Person.prototype.sayName = function() {
console.log(this.name);
}
const p = new Person('orange')
console.log(p) // { age: 35 }
console.log(p.name) // undefined
p.sayName(); // TypeError: p.sayName is not a function
/**
* --- Person 返回非对象,return 不影响结果 ---
*/
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
return 'free'
}
Person.prototype.sayName = function() {
console.log(this.name);
}
const p = new Person('orange')
console.log(p) // Person { name: 'orange' }
console.log(p.name) // orange
p.sayName(); // orange上面的例子中,如果返回了一个对象,我们需要返回该对象;如果不是对象,则 return 没用,正常处理。
5. 如何自己实现一个 instanceof?
答案
/*
* --- 手动实现 instanceof ---
*/
function newInstanceOf (leftValue, rightValue) {
if (typeof leftValue !== 'object' || rightValue == null) {
return false;
}
let rightProto = rightValue.prototype;
leftValue = leftValue.__proto__;
while (true) {
if (leftValue === null) return false;
if (leftValue === rightProto) return true;
leftValue = leftValue.__proto__;
}
}
/*
* --- 验证 ---
*/
const a = [];
const b = {};
function Foo () {}
var c = new Foo()
function Child () {}
function Father() {}
Child.prototype = new Father()
var d = new Child()
console.log(newInstanceOf(a, Array)) // true
console.log(newInstanceOf(b, Object)) // true
console.log(newInstanceOf(b, Array)) // false
console.log(newInstanceOf(a, Object)) // true
console.log(newInstanceOf(c, Foo)) // true
console.log(newInstanceOf(d, Child)) // true
console.log(newInstanceOf(d, Father)) // true
console.log(newInstanceOf(123, Object)) // false
console.log(123 instanceof Object) // false解读
这个问题既考察了 instanceof 的原理,又考察了原型链,还考察了代码能力,是一个好问题。
在实现代码中,我们判断 leftValue 是否为 rightValue 的实例,思想是在 leftValue 的原型链上,即 leftValue.__proto__ 上寻找是否存在 rightValue.prototype。原理图如下:
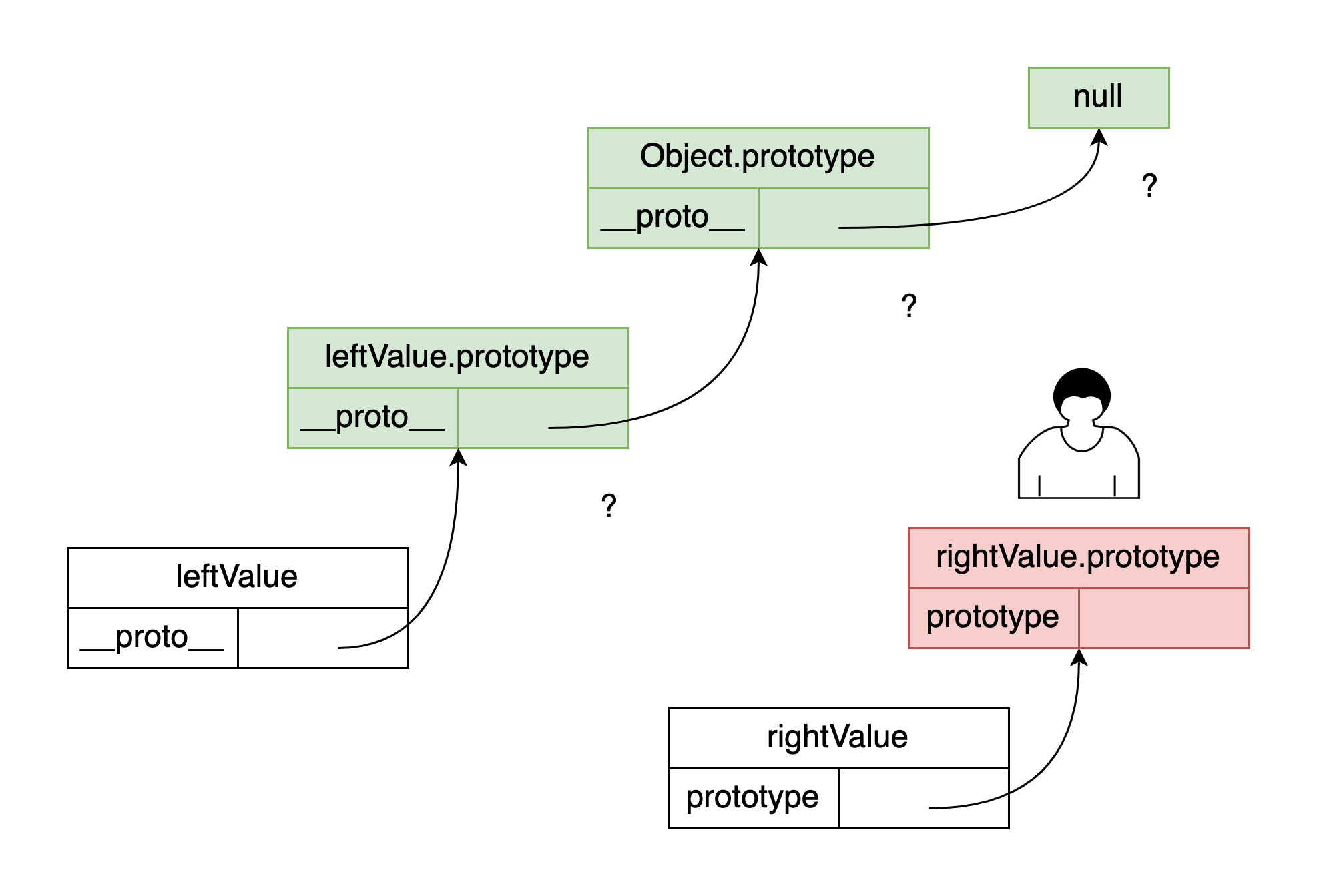
这需要我们熟练掌握原型链的相关知识。
6. 实现 Promise.all()
引用 :
Promise.all(iterable)方法返回一个Promise实例,此实例在iterable参数内所有的promise都“完成()”或参数中不包含promise时回调完成();如果参数中promise有一个失败(),此实例回调失败(),失败的原因是第一个失败promise的结果。
function promiseAll(promises) {
return new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
if (!isArray(promises)) {
return reject(new TypeError('arguments must be an array'));
}
var resolvedCounter = 0;
var promiseNum = promises.length;
var resolvedValues = new Array(promiseNum);
for (var i = 0; i < promiseNum; i++) {
(function(i) {
Promise.resolve(promises[i]).then(function(value) {
resolvedCounter++
resolvedValues[i] = value
if (resolvedCounter == promiseNum) {
return resolve(resolvedValues)
}
}, function(reason) {
return reject(reason)
})
})(i)
}
})
}应用类
1. 手写防抖(debounce)
// debounce
function debounce(fn, delay=500) {
// timer 写在闭包中,因此防抖也是闭包的一个应用
let timer = null;
return function() {
if (timer) {
clearTimeout(timer)
}
timer = setTimeout(() => {
fn.apply(this, arguments);
timer = null;
}, delay)
}
}
// 验证
input1.addEventListener('keyup', debounce(() => {
console.log(input1.value);
}), 600)2. 手写节流(throttle)
// 节流
function throttle(fn, delay = 100) {
let timer = null
return function() {
if (timer) {
return
}
timer = setTimeout(() => {
fn.apply(this, arguments)
timer = null
}, delay)
}
}
div1.addEventListener(('drag', throttle(function (e) {
console.log(e.offsetX, e.offsetY)
})))3. DOM 题目
假设一个
ul下有一万个li,li的innerHTML是从0到9999,当点击某个li时输出该li代表的值,如何实现
答案
采用事件委托:
window.onload = function () {
var uli = document.getElementById("ul");
uli.onclick = function(event) {
alert(event.target.innerText);
}
}解读
首先,我们当然不可能为每一个 li 标签手动添加一个 click 事件(容易累死);其次,我们可能会想到使用 for 循环遍历每个元素,然后为其添加 click 事件,但这样会频繁操作 DOM,降低性能,卡到爆炸。
而事件委托意义就在于此:减少 DOM 操作,从而减少浏览器的重绘与重排次数,提升性能。
事件委托的原理是,将 li 上监听的 click 事件委托到 ul 上。这里运用到了 事件冒泡 的机制,即 onclick 事件以 li -> ul -> body -> html -> document 的冒泡顺序逐步传递。
所以,我们可以选择在其中的 ul 上监听 click 事件,从而实现事件委托。
如何创建 100000 个
<li>呢?总不能复制粘贴 100000 次吧?
创建 个 <li> 标签,思路是将 保存在数组中,然后转化为字符串 "<li>0</li><li>1</li>...<li>9999</li>",最后将他们作为 ul 标签的 innerHTML 即可。
/* --- create100000li.js --- */
window.onload = function() {
var ul = document.getElementsByTagName("ul");
var arr = [];
for (let i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
arr.push(i);
}
ul[0].innerHTML = '<li>' + arr.join('</li><li>') + '</li>'
}4. 手写 Promise 加载一张图片
function loadImg(src) {
const p = new Promise(
(resolve, reject) => {
const img = document.createElement('img')
img.onload = () => {
resolve(img)
}
img.onerror = () => {
const err = new Error(`图片加载失败 ${src}`)
reject(err)
}
img.src = src
}
)
return p
}
const url = 'https://pic.leetcode-cn.com/1604237471-xbJgZl-%E5%9B%BE%E7%89%871.png';
loadImg(url).then(img => {
console.log(img.width)
return img
}).then(img => {
console.log(img.height)
}).catch(ex => console.error(ex))5. 如何用 原生实现一个 post 请求
答案
function ajax_post(url, data) {
// 1. 异步对象 ajax
var ajax = new XMLHttpRequest();
// 2. url 方法
ajax.open('post', url);
// 3. 设置请求报文
ajax.setRequestHeader('Content-type', 'text/plain');
// 4. 发送
if (data) {
ajax.send(data);
} else {
ajax.send();
}
// 5. 注册事件
ajax.onreadystatechange = function () {
if (ajax.readyState === 4 && ajax.status === 200) {
console.log(ajax.respenseText);
}
}
}6. 每隔一秒输出一个数字
for (let i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(i);
}, 1000 * i)
}7. 判断两个对象是否相等
/*
* @param x {Object} 对象1
* @param y {Object} 对象2
* @return {Boolean} true 为相等,false 为不等
*/
console.log(_.isEqual(x, y))实现代码中,以下边界情况无法处理:
- 其中某个属性本身是一个对象
- 某个属性的值为
NaN - 一个对象的属性的值为
undefined,另一个对象中没有这个属性
对于所有边界情况的处理,请参考 Lodash 中的 _.isEqual( ) 源码
